Introduction
Ego is an open-source OAuth 2.0/OpenID application that simplifies user management by providing methods to authenticate (establish who a user is) and authorize (establish what a user is allowed to do) users of your application through well-known social Single-Sign-On identity providers like ORCID or Google. Ego provides stateless authorization using JWT (JSON Web Tokens) and can scale very well to a large number of users.
Authentication
Ego allows users to login and authenticate themselves using the well-known and secure OAuth 2.0 protocol. Ego does not manage usernames and passwords, but instead relies on popular identity provider to complete this. Supported integrations include:
- ORCID, a well established "research" identity passport
- Github
Authorization
Once users are authenticated, are granted tokens that encode permissions to access resources. Ego supports:
- User API Keys
- User JWT's
- Appliation JWT's Secured applications can create and manage authorization tokens, and use those tokens to interact with third party applications registered in Ego to manage resource authorization.
Permissions can be managed based on Applications, Groups, or can be directly assigned to Users.
UI Managemet
In addition to the coprehensive API, Ego is complemented by a UI application to make user management even easier. UI User Documentation explains how to accomplish the ost popular use cases.
How Ego Works
Once ego has been setup, Ego resolves a user or application identity with the permissions that they have been granted, either directly or inherited through a group. Permissions are encoded in a secret authorization JWT (Json Web Token), that has a limited life.
Downstream services make a REST call to EGO to determine the user and authority represented by a JWT, or can accept a JWT and decided from the encoded information if a user or application is allowed to take a certain action.
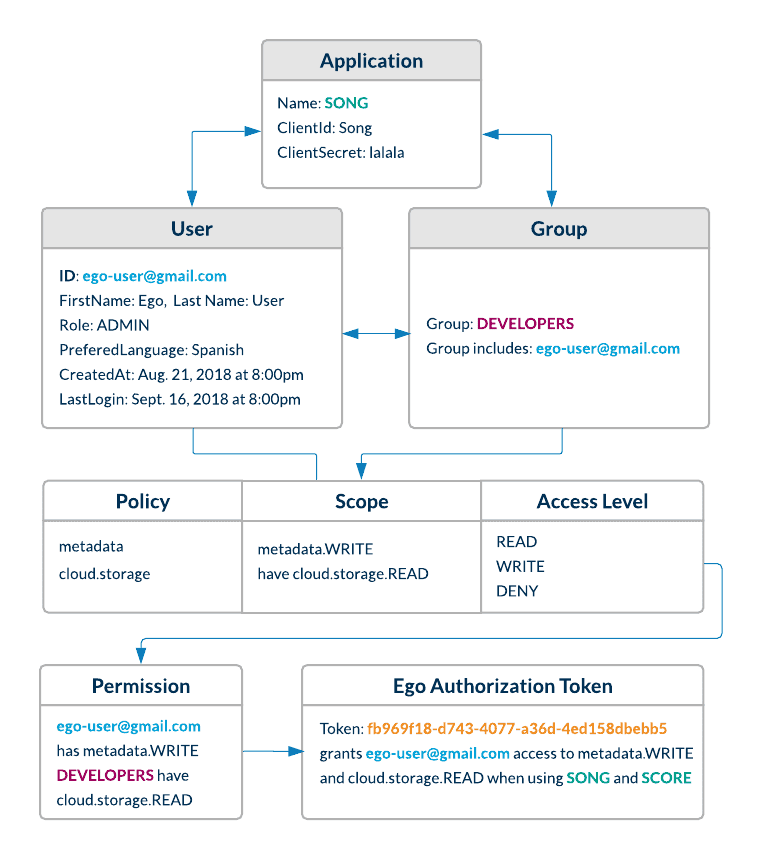
Definitions
| Entity | Description |
|---|---|
| User | A user is any individual registered in Ego who needs to authorize themselves with Ego-aware applications. |
| Admin | An admin is a power user whose role is set to ‘ADMIN’. Only admins are authorized to register users, groups, applications & policies using Ego’s REST endpoints. |
| Group | A group of users with similar properties. Admins can create new groups and add users to them. They can then assign permissions to an entire group which will be reflected for each user in that group. |
| Policy | A policy is a scope or context for which an application may want to grant a user or group READ/WRITE/DENY permissions. |
| Permission | A user or group can be given READ/WRITE/DENY permissions for a particular policy. |
| Application | An application is a third party service that registers itself with EGO so that EGO can authorize users on its behalf. Upon registration, the service must provide a client_id and client secret. |
| Application Authentication Token | This a Basic JWT token which encodes a client id and secret, and authorizes an application to interact with Ego. This is passed in the authorization request header when an application uses the check_token endpoint in order to check a user’s token. |
| User Authentication Token | This is a Bearer token which encodes user information, and is passed to a user when they are authenticated through OAuth single sign-on. This Bearer token is passed in the request authorization header whenever the user wants to access Ego’s resources. If the JWT denotes that a user has an ADMIN role, they are permitted to create and modify resources (users, groups, permissions, policies). |
| User Authorization Token | This is a random token which is generated to authorize a user for a specific scope, in the context of an application. |